555 Contest Entry: Motion activated camera
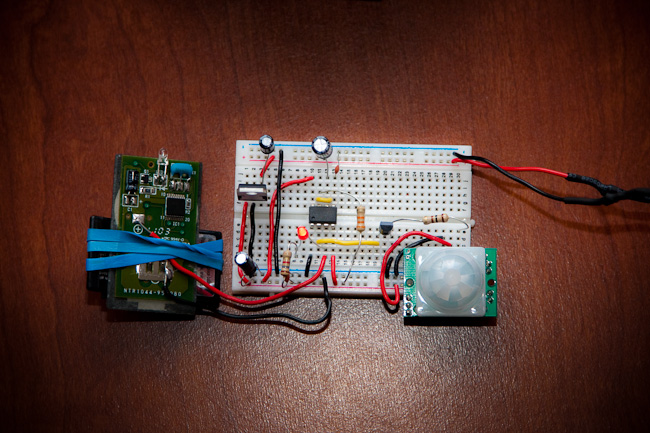
This entry for the 555 timer contest is from Andrew Smith who built a motion activated switch for a digital camera. The 555 timer is operating in monostable mode which is triggered by a PIR sensor when motion is detected. The monostable output of 555 then activates the camera through a remote.
Read more