Tiva C tutorials
These Tiva C tutorials are contributed by Shawon Shahryiar, a technologist, hardware maker, educator and EEE graduate from Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology, Dhaka.
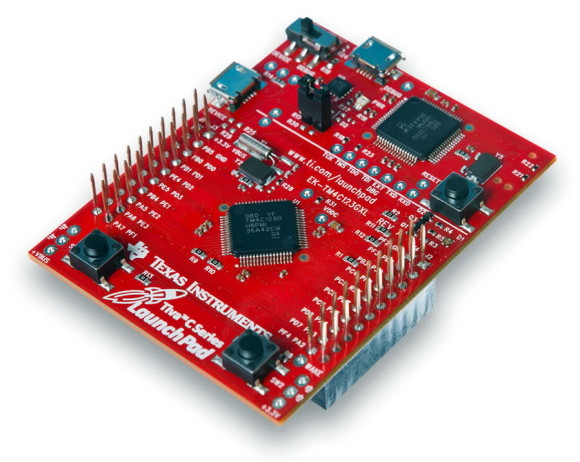
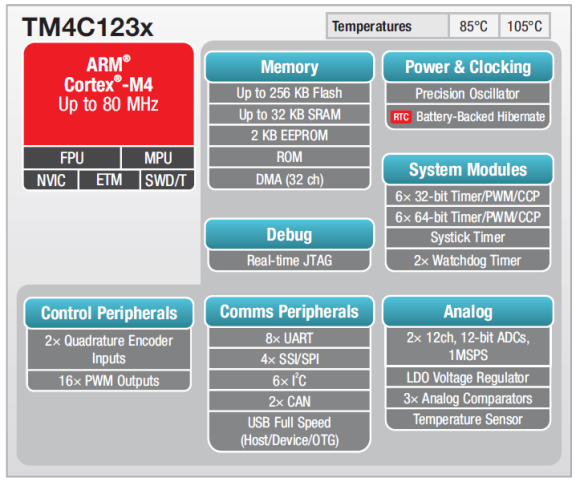
Most of us who work with electronics know the name of Texas Instruments (TI) as a manufacturer of several important digital and analogue ICs as well as fancy sophisticated scientific calculators. However many people don’t know that TI is also a manufacturer of some of industry’s best microcontrollers. TI’s portfolio of micros is pretty large. ARM micros are getting popular day-by-day and on that family of micros TI has some of the best devices one can imagine. One such family from TI is the Tiva C series. Enter the TM4C123x Tiva C micros – one of the best possible combination of high-end hardware ever integrated with an ARM Cortex M4.
The clock system of a microcontroller is a fundamental element. Clock system provides the heart-beat needed to keep applications running in a synchronous manner. In the case of Tiva C micros the clock system is as much as sophisticated and elaborate as with any other ARM micros. In this post we will explore this basic block of Tiva C micros. We will see that the clock system is a network of different clock sources and internal units that are intertwined in a complex but easy manner.
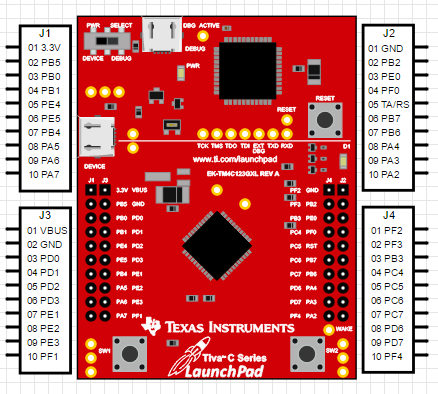
GPIOs are the basic interfaces of any microcontroller. Without GPIOs we won’t have any other way to use a micro and it will be nothing more different than a chunk of well-fabricated silicon. Through them we can interface both transducers or sensors and actuators. We can also connect other devices like a display, external devices and so on. As with any ARM microcontroller, the GPIOs of TM4C12x Tiva C ARM microcontrollers are very elaborate, having many options that are usually unavailable in common 8-bit microcontrollers.
|
|