Proper PCB grounding for mixed-signal designs
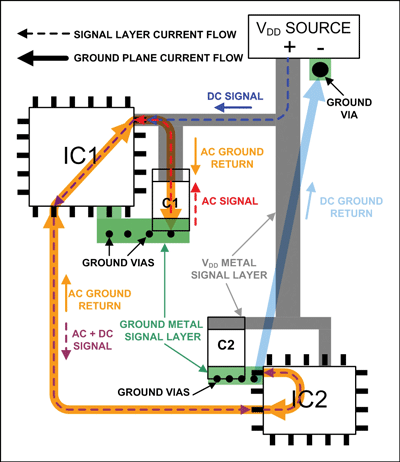
Circuit board designers have always concerns about the proper way to handle grounding for integrated circuits (ICs), which have separate analog and digital grounds. This tutorial from MAXIM integrated discusses proper printed-circuit board (PCB) grounding for mixed-signal designs. For most applications a simple method without cuts in the ground plane allows for successful PCB layouts with this kind of IC. Next, we learn how to place components and route signal traces to minimize problems with crosstalk. Finally we move on to consider power supply-currents and end by discussing how to extend what we have learned to circuits with multiple mixed-signal
Read more