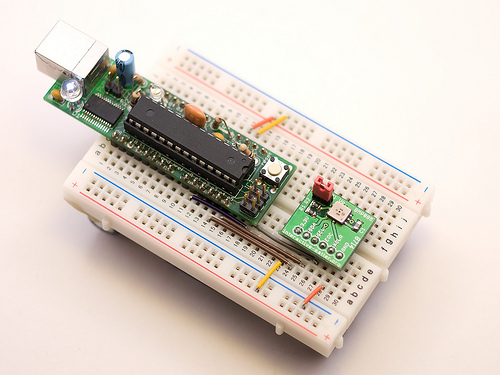
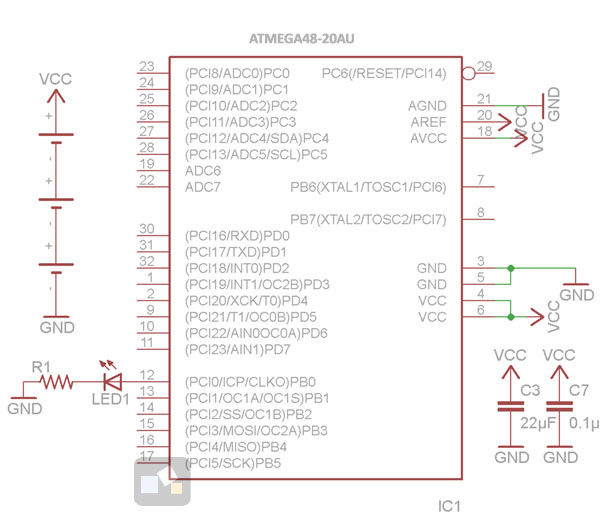
How would a microcontroller know how it’s own supply voltage is changing? Well, most microcontrollers have built in analog-to-digital converters that can read an input analog voltage and convert it to a digital number. So, it might be suggestive to use a similar technique. But the problem is, any ADC operation requires a reference voltage, which in most cases, is either the source voltage or one derived from it. So, how would you monitor the source voltage through ADC that uses the same source voltage as reference?
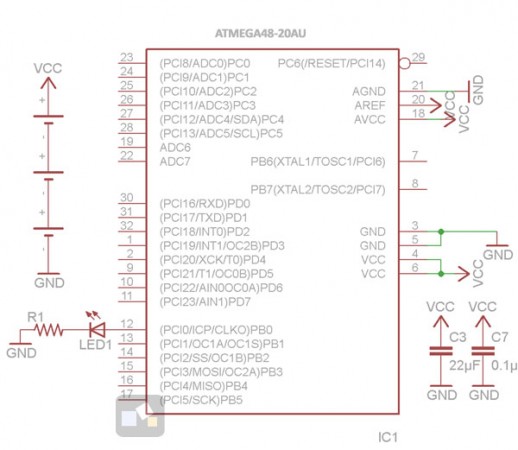
The following article describes a way to do this without using any additional external components. It uses the internal band gap reference voltage of an AVR microcontroller to correct any error in the measurement of the supply voltage through the built in ADC. The band gap voltage of AVR is fixed 1.1 V that you can feed to ADC input using software. You know what would be the ADC output for this fixed band gap input voltage, with the known supply voltage as reference. If you find any drift in the measurement output, you can calculate the drift in the reference voltage, and so in the supply voltage.