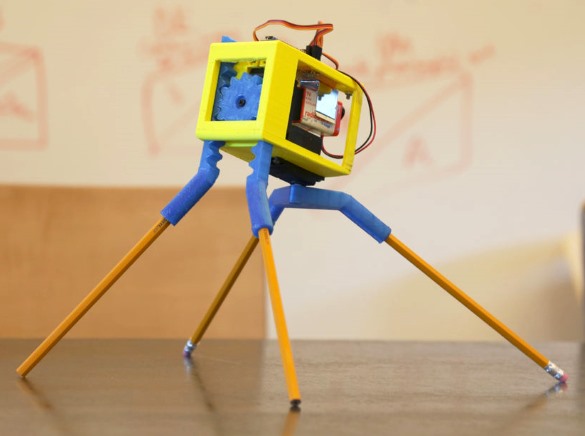
3-D printed walking robot

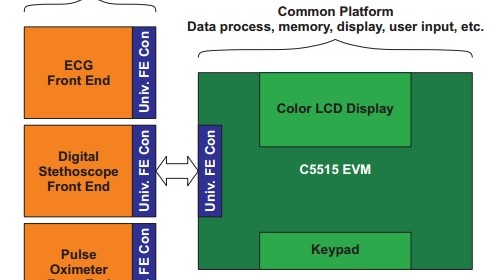
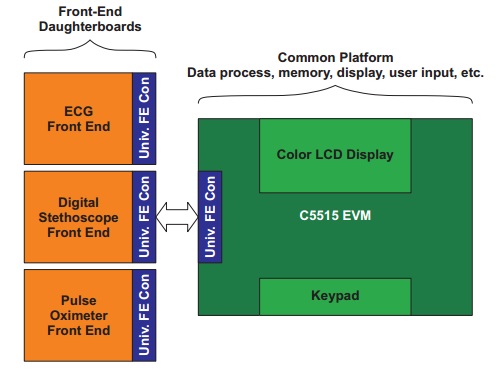
One of the most interesting applications of 3-D printing technology is building customized robot parts. It allows makers to design their own parts on a computer using affordable tools and convert the design into an actual physical product in just a few hours. Randy’s 3-D printed walking robot is a great example of 3-D printing robot parts for rapid prototyping and implementation of your ideas. The robot uses two standard servos for locomotion and are controlled by Arduino. The author also shares his 3-D printer design files and Arduino sketch to the public.