Arduino: Digital energy monitor for your house
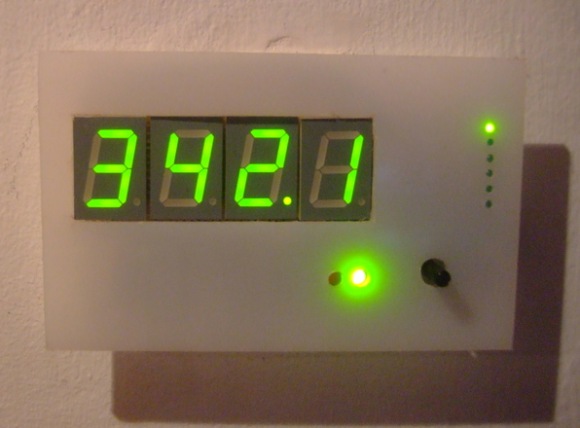

This project describes a whole house energy monitor that provides quick access to current energy use information, usb datalogging for detailed long term data storage and Internet connectivity for online graphing. The display unit uses four seven-segment LED displays that shows real power, apparent power, power factor, RMS voltage, RMS current, frequency and cumulative KWH consumed.
Read more