Lab 5: Analog-to-digital conversion (ADC)
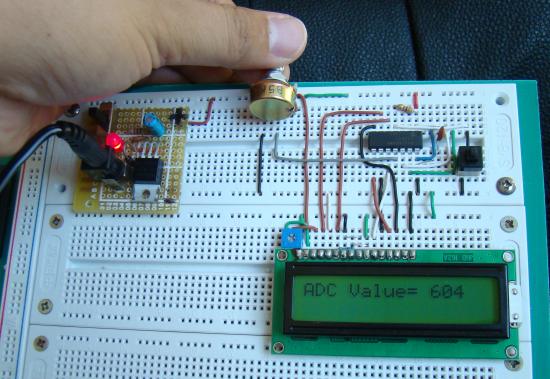
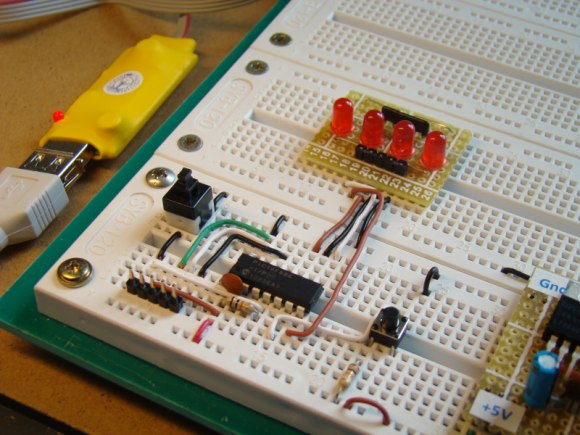
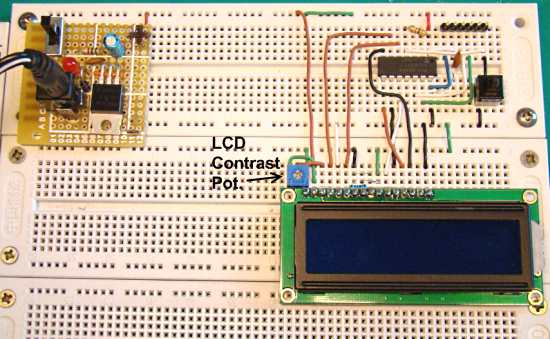
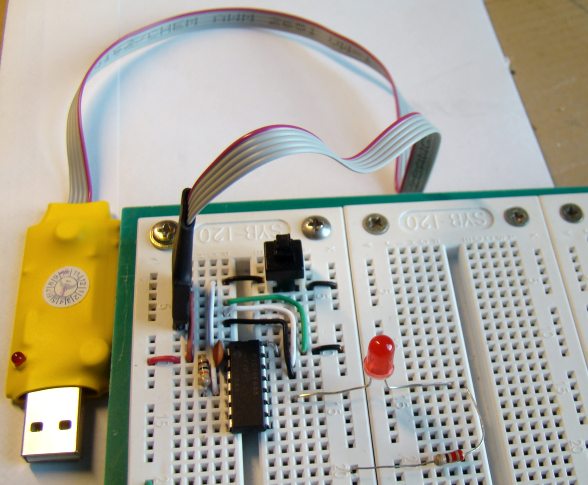
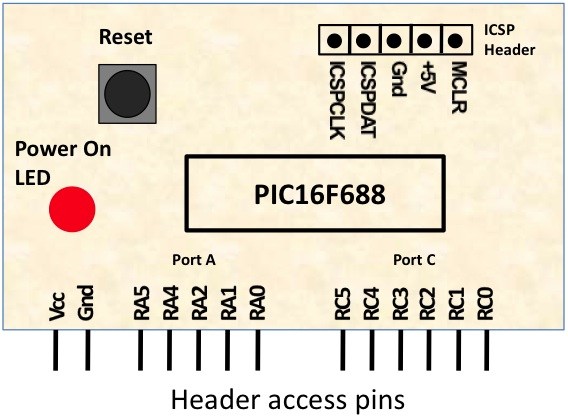
Description Analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) is necessary because, while embedded systems deal with digital values, their surroundings typically involve many analog signals such as, temperature, speed, pressure, the output of a microphone, etc. They all need to be converted into digital data before being processed by the microcontroller. Today, we will see how to read an external analog signal using a PIC16F688 microcontroller, and display the conversion output (a digital number) on a LCD. The input analog signal will be a varying voltage between 0-5V derived using a potentiometer. Required Theory The PIC16F688 microcontroller has a built-in 10-bit ADC with eight
Read more