Lab 14: Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) communication
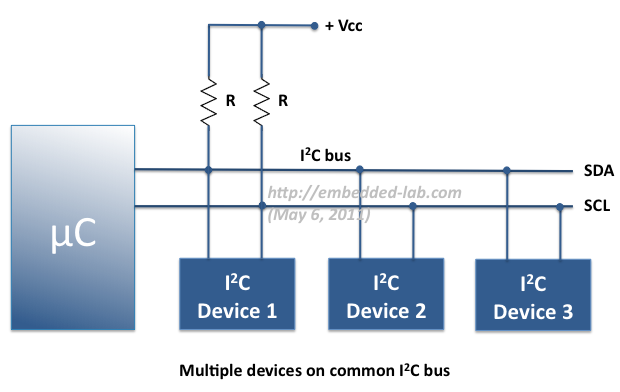
I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) is a short distance serial interface that requires only 2 bus lines for data transfer. It was invented by Philips in 1980’s, originally to provide easy on-board communications between a CPU and various peripheral chips in a TV set. Today, it is widely used in varieties of embedded systems to connect low speed peripherals (external EEPROMs, digital sensors, LCD drivers, etc) to the main controller. In this experiment, we will cover an overview of I2C protocol, its implementation in PIC microcontrollers, and the method of connecting single and multiple devices on a common I2C bus. We will
Read more