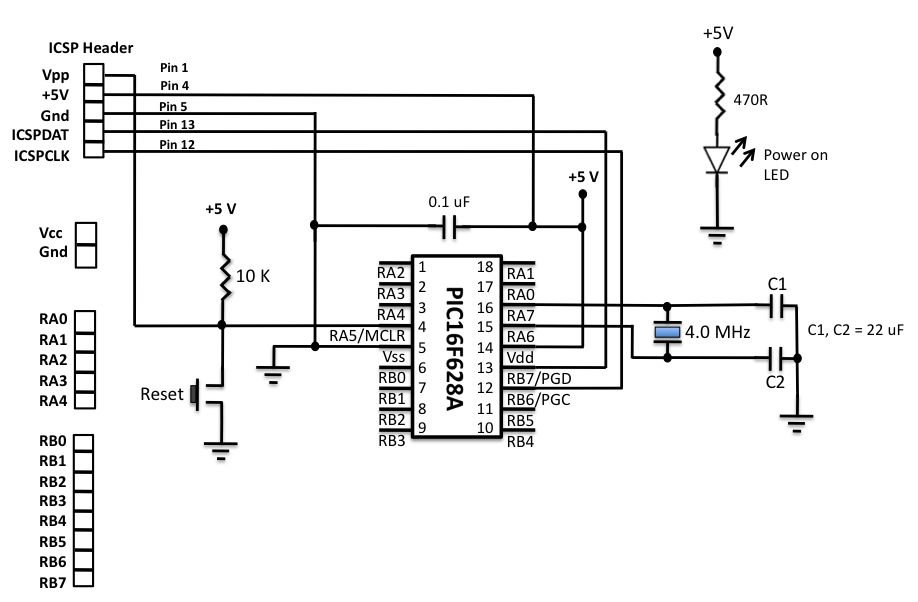
Monochrome Composite Video using Atmega8
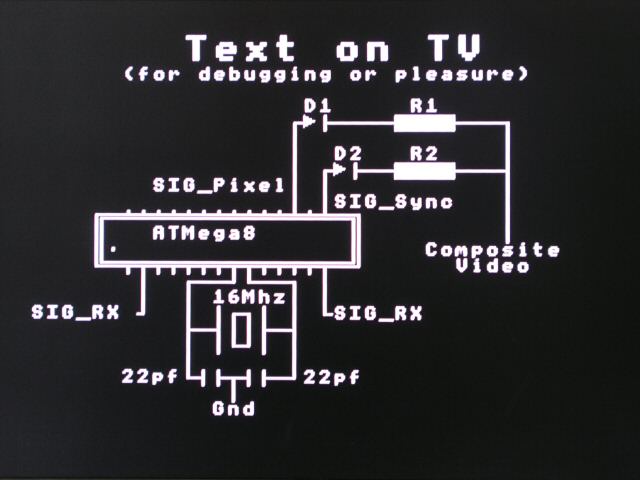
This article describes the design of a Text on TV project. It takes serial data and displays text on a TV screen. The hardware part of this project is pretty simple. It uses an Atmega8 microcontroller that runs with a 16 MHz crystal. The article provides the details on PAL and NTSC timing signals, as well as how to implement the signals in software.
Read more