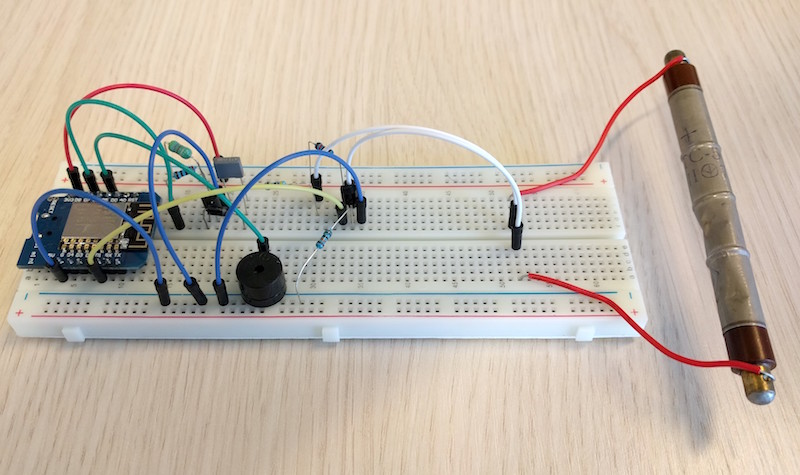
ESP8266 powered DIY Geiger Counter
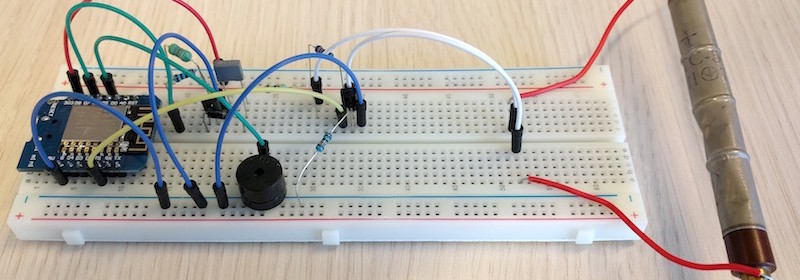
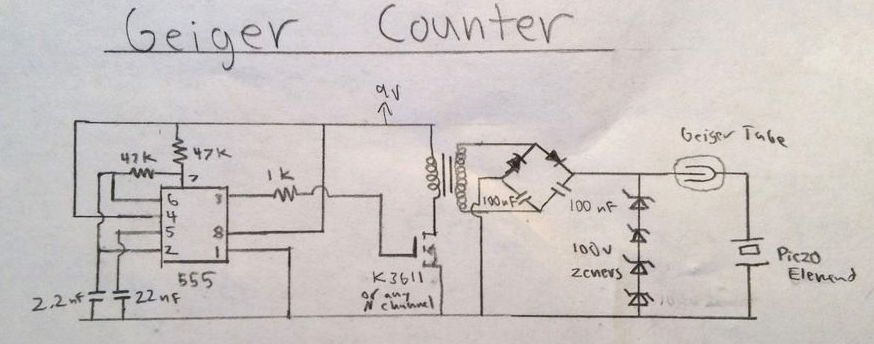
DIY Geiger counter projects are very popular among hobbyists. They all use a Geiger-Muller (GM) tube, which is filled with an inert gas such as helium, neon, or argon at low pressure, to which a high voltage is applied. The tube becomes electrically conductive when it is impacted by a high-energy particle or photon. Earlier, we have seen a very simple Geiger counter circuit using 555 timer, where the timer IC is configured as an astable multivibrator to drive a step-up transformer through a MOSFET in order to generate the high voltage required for the GM tube. This ESP8266-powered DIY Geiger counter by Hackaday user biemster, however, avoids the use of any step up transformer for the high-voltage generation; it rather achieves the same using a simple MOSFET switching circuit comprising of an inductor, a diode and a capacitor. The switching circuit is driven by a PWM waveform from an ESP8266 I/O pin. The use of ESP8266 also provides network connectivity to access the radiation and dose information via web interface, MQTT, or ICMP packets.
The high voltage output from the MOSFET switching circuit depends on the duty cycle of the PWM signal, which can be adjusted in the software. The complete code for this project can be downloaded from Github. LTspice simulation results showed that with a PWM frequency of 10 kHz, the output voltage has minimum ripple on it. The PWM generation, ESP8266 pin assignments, and calibration of the duty cycle to derive an optimal high-voltage output for the tube are all provided by the author in one MicroPython library.