Lab 20: Interfacing a KS0108 based Graphics LCD (Part 1)
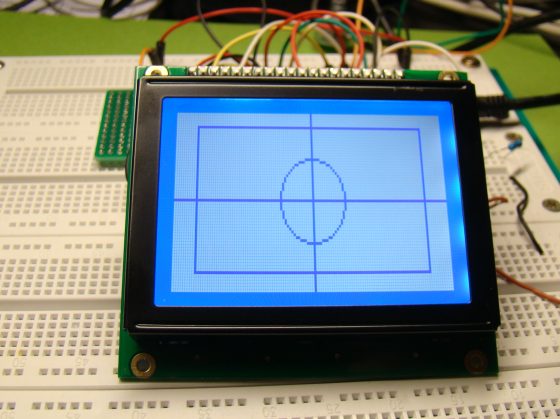
The use of a graphical LCD (GLCD) drastically changes the look of your project. It provides more freedom for presenting data than the HD44870 based character LCDs. Today we will see how to interface a KS0108 (name of the display controller chip) based GLCD to a PIC microcontroller. This experimental tutorial is divided into two parts. In the first part, we will see how to write a firmware for the PIC microcontroller to initialize the GLCD and send data to plot points and lines on the screen. The second part will focus more on exploring the built-in GLCD Library of mikroC Pro for PIC compiler to display more complex texts and objects. Since GLCDs are real resource hungry devices (in terms of required I/O pins and memory), a bigger size PIC microcontroller (PIC16F887, which has 36 I/O pins and 14KB flash memory) is selected for this experiment. I am using MikroElektronika’s UNI-DS6 development board to demonstrate this project, but the circuit setup can also be made on a breadboard.