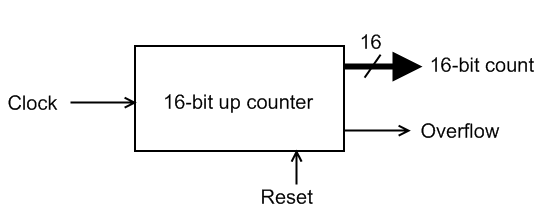
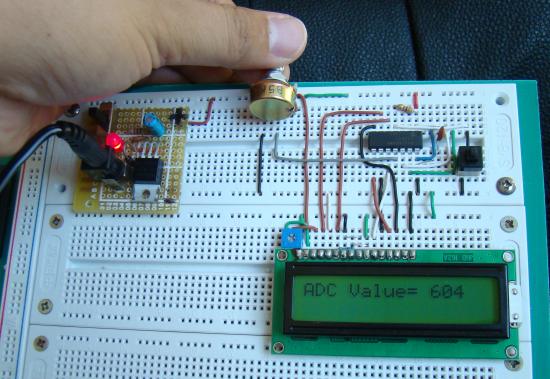
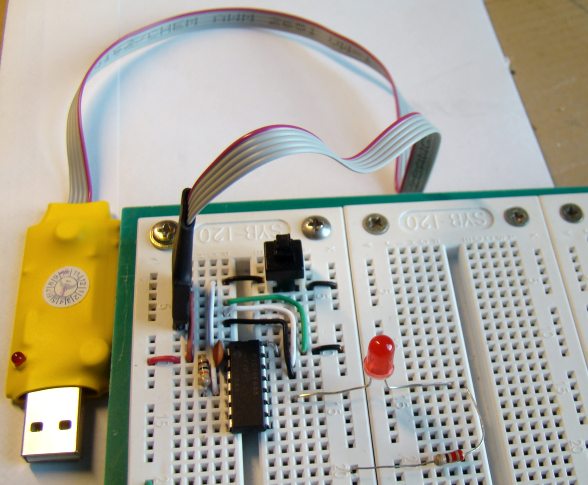
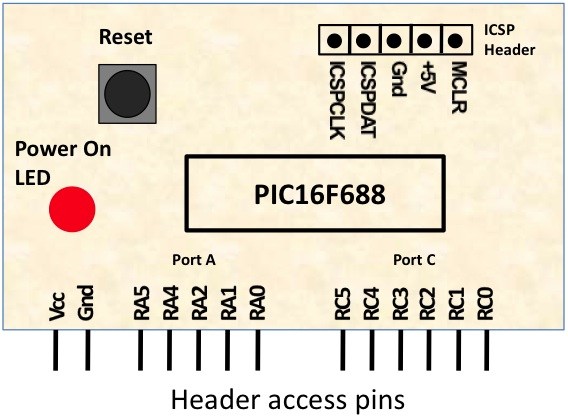
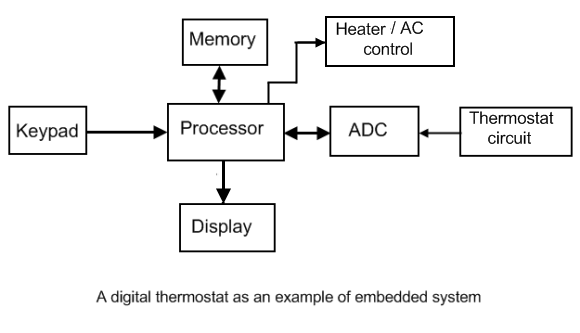
Overview of an Embedded System
Computer systems are everywhere. They fall into essentially two separate categories. The first and most obvious is that of the desktop computer. This is the machine that first comes in our mind when we talk about computers. Desktop computers are designed to be flexible and to meet a wide range of user needs. The end users can change the functionality of a desktop computer by simply changing the application program. One moment you may be using it as a word processor, the next you as an mp3 player or a game station. The second type of computer is the embedded computer
Read more