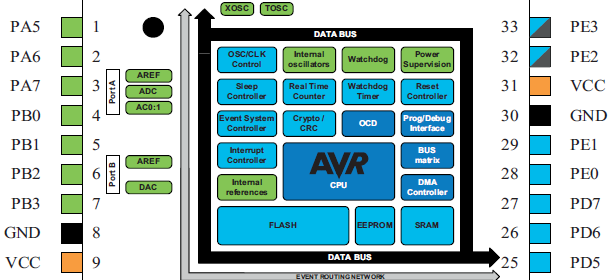
XMega Clock System
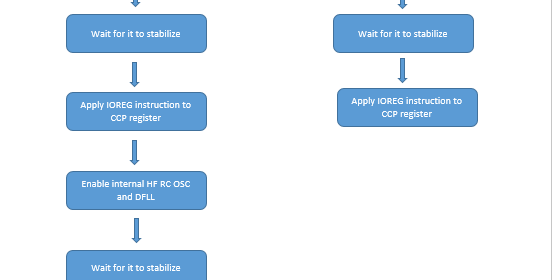
Okay firstly the reason I wrote about the clock system instead of I/O ports or something else in this second post of the XMega series is simply because of the fact that without understanding clock configurations you won’t get what you want from your chip. Since XMega’s clock system is software-level configurable and complex at first, it makes itself the first priority module before anything else. There are several clock sources that XMega micros can use as clock. These are both internal and external clock sources. As stated earlier, clocks are not set by fuse settings unlike traditional Mega AVRs,
Read more