Humidity and temperature measurements with Sensirion’s SHT1x/SHT7x sensors (Part 2)
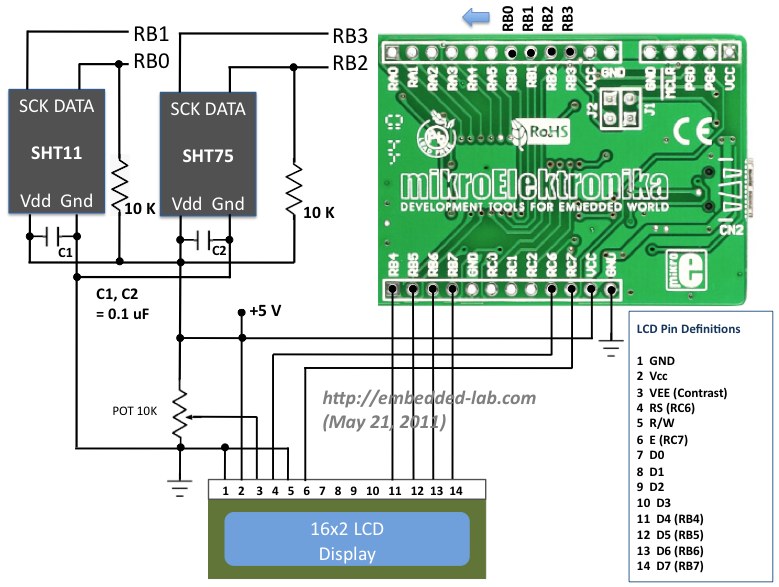
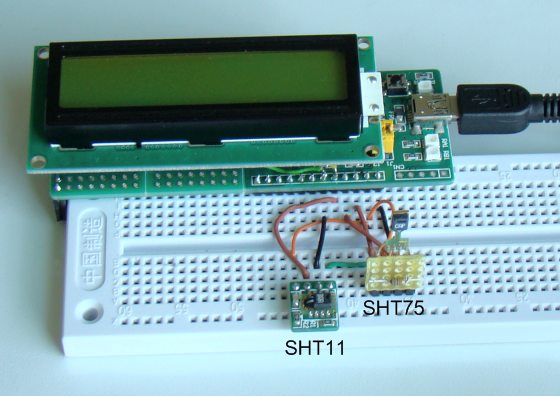
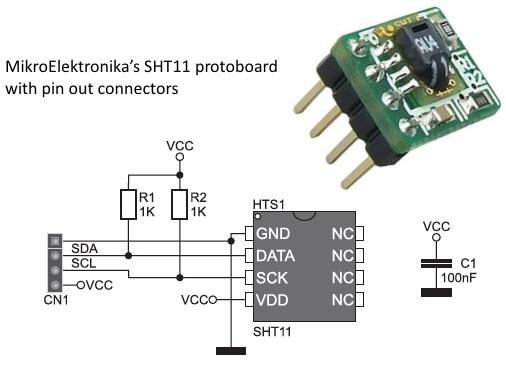
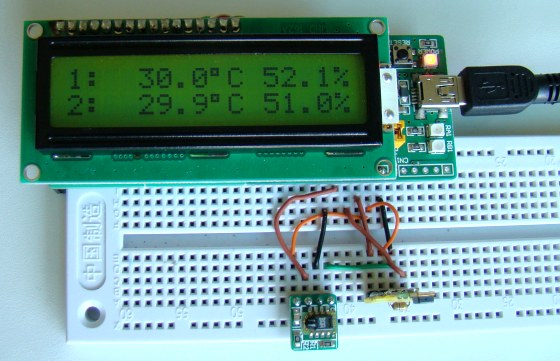
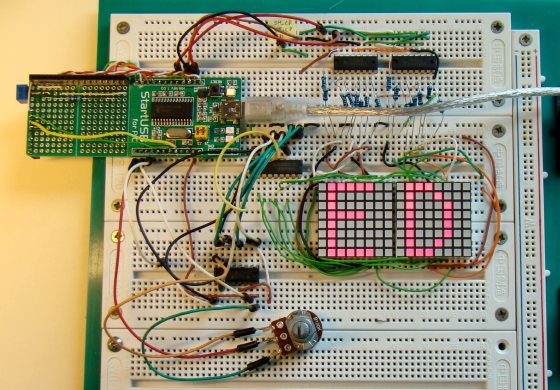
In Part 1 of this tutorial, we discussed about Sensirion’s SHT1x and SHT7x series of humidity sensors, their interface specifications, the communication protocol used for transferring data in and out of the sensor, and the equations to convert their digital outputs to actual physical quantities. These sensors are capable of measuring temperature along with relative humidity and provide outputs in fully-calibrated digital words. We will now see how a PIC microcontroller can be programmed to communicate with these sensors, read the temperature and relative humidity data, and display the information on a character LCD.