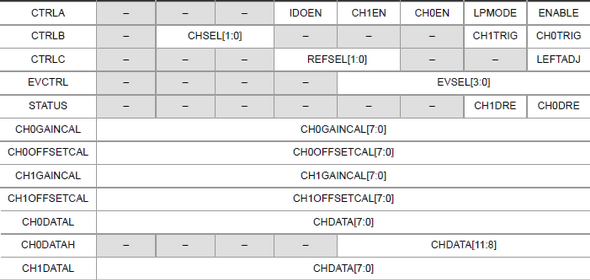
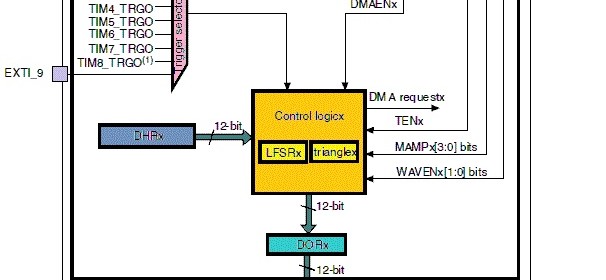
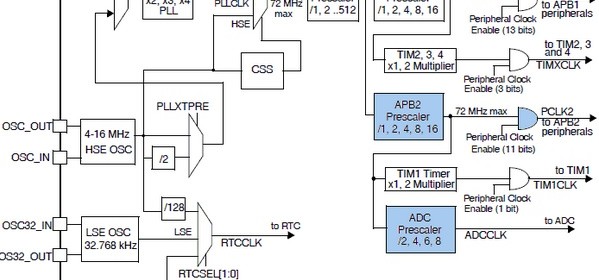
Hookup guide for 16×32 RGB LED panel – Part 1

RGB LED panels are a great way of displaying colorful texts, images, and animation. In this 3-part tutorial, I am going to demonstrate how to hookup our 16×32 RGB LED panel kit to an Arduino Uno board and run some demo sketches. Our 16×32 RGB LED matrix panel kit includes everything you need to connect it to an Arduino Uno board. The kit includes: One 16×32 RGB LED matrix panel One RGB connector shield for Arduino Uno One IDC cable to connect the RGB matrix panel to the RGB shield One power supply connector for the RGB matrix Note that the power supply
Read more