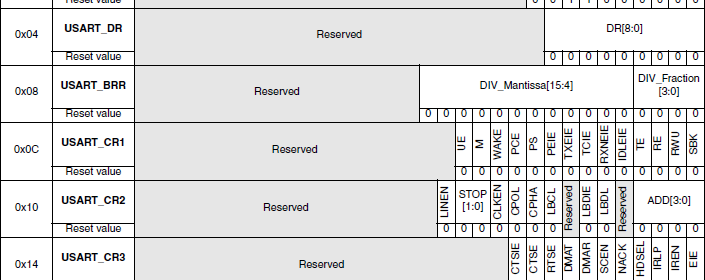
STM32 Internals
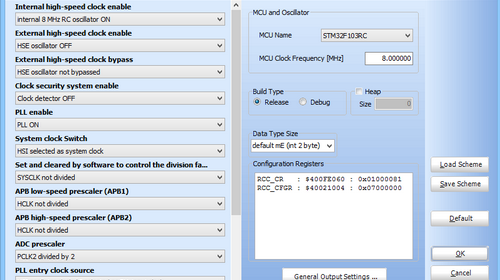
STM32 micros as we know are high-end micros and this high-end tag is not only due to its memory, speed and hardware richness. An advanced micro like this also needs advanced internal supporting hardware. Most of us know about watchdog timers from previous experiences with common 8 bit MCUs like AVR and PIC. However when it comes to STM32 the idea of watchdog circuitry is elaborated. The options available for clock are also enhanced in the STM32 micros. In this post, we will see some of these supporting internal hardware. We will examine the use and operation of two different
Read more