chipKIT Tutorial 5: Pulse width modulation (PWM)
|
|
Pulse width modulation (PWM) is a technique of controlling the amount of power delivered to an electronic load using an on-off digital signal. The key idea behind this technique is that the average DC value of the digital signal, and hence the power delivered to the load, can be varied by varying the duty cycle of the signal. This method is commonly used for controlling speeds of DC motors and brightness of lamps. The switching mode power supplies are also based on the PWM technique. In this tutorial, we will discuss about the PWM pins of the chipKIT Uno32 board and illustrate the concept by controlling the brightness of two external LEDs.
Theory
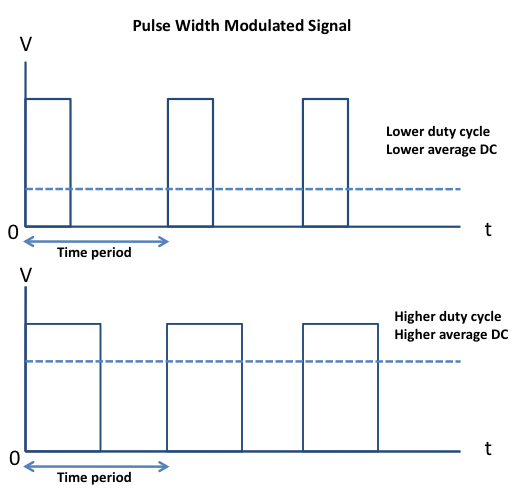
Pulse-width modulation (PWM) is a way of delivering energy through a succession of pulses rather than a continuously varying signal. By increasing or decreasing the pulse width (while frequency remaining unchanged), it is possible to control the output power. The fraction of the period for which the signal is on is known as the duty cycle. The average DC value of the signal can be varied by varying the duty cycle. The duty cycle can be anywhere between 0 (signal is always off) to 1 (signal is constantly on). Suppose, if the signal has +5 V while it is on and 0 V during off condition, then by changing the duty cycle of the signal, any voltage between 0-5 V can be simulated. This method is commonly used for controlling speeds of DC motors and brightness of lamps. The principle of PWM is illustrated in the picture below.
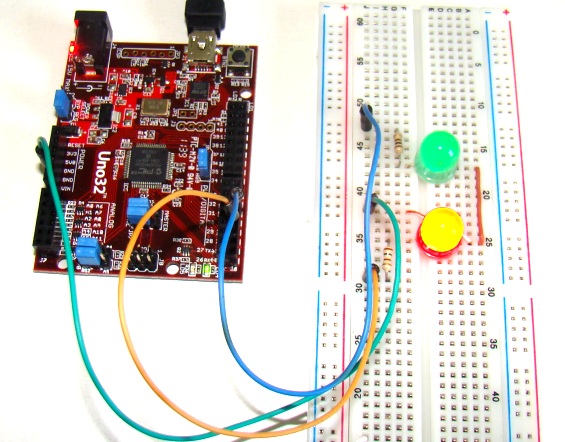
Circuit setup
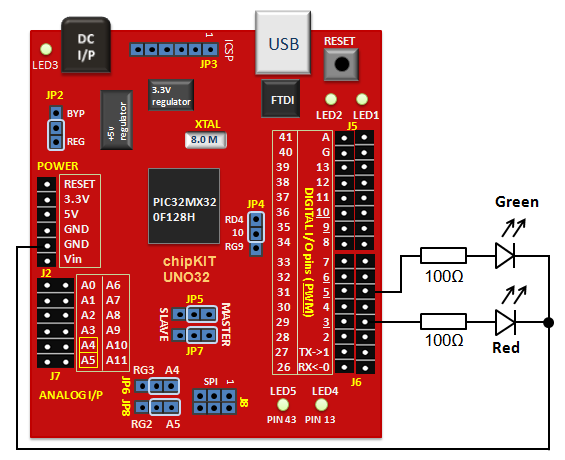
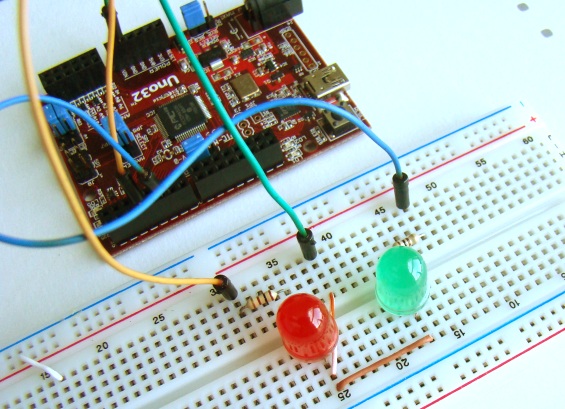
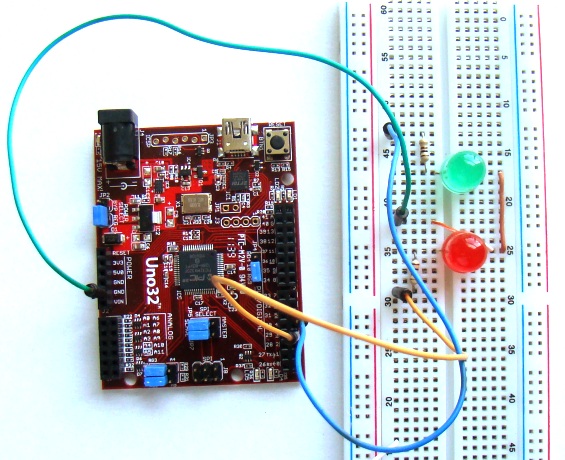
On chipKIT Uno32 board, the I/O pins 3, 5, 6, 9, and 10 can be configured to provide PWM outputs. We will connect two LEDs (red and green) to PWM pins 3 and 5 and control their brightness by varying the duty cycles of the PWM signals driving those LEDs. Two 100? resistors are used to limit the current through the LEDs.
Writing sketch
PWM signals in an Arduino platform can be generated using analogWrite() command. Inside the parenthesis, you specify the pin number and the desired duty cycle (0-255). Duty cycle of ‘0’ corresponds to always off and ‘255’ corresponds to always on. When the analogWrite() is called, a steady square wave with the specified duty cycle is generated at the specified PWM pin. The following sketch controls the output power delivered to the two LEDs using varying duty cycle PWM signals. The two LEDs fade in and out alternately, which means when one is at peak intensity, other is dimmed low, and vice-versa.
int redLED = 3; // Red LED is connected to pin 3 int greenLED = 5; // Green LED is connected to pin 5 int redCount = 255; // Initial PWM values, RED is full int greenCount = 1; // Green is dim int i = 0; void setup() { pinMode(redLED, OUTPUT); pinMode(greenLED, OUTPUT); } void loop() { if (i < 255) // First phase { redCount = redCount-1; // Red down greenCount = greenCount+1; // Green up } else if (i < 509) // Second phase { redCount = redCount+1; // Red up greenCount = greenCount-1; // Green down } else // Re-set { i = 0; } i += 1; analogWrite(redLED, redCount); // Write current values to LED pins analogWrite(greenLED, greenCount); delay(10); // Pause for 10 millisecond } |
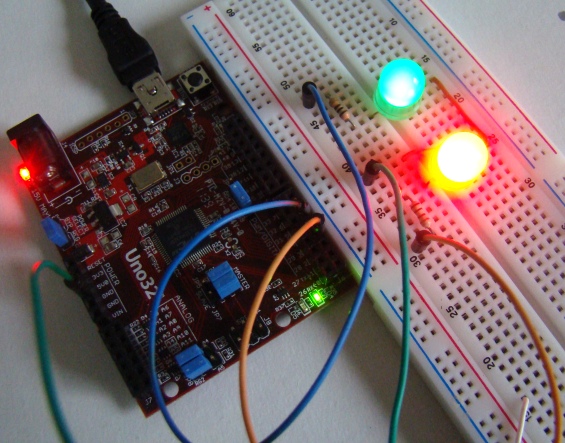
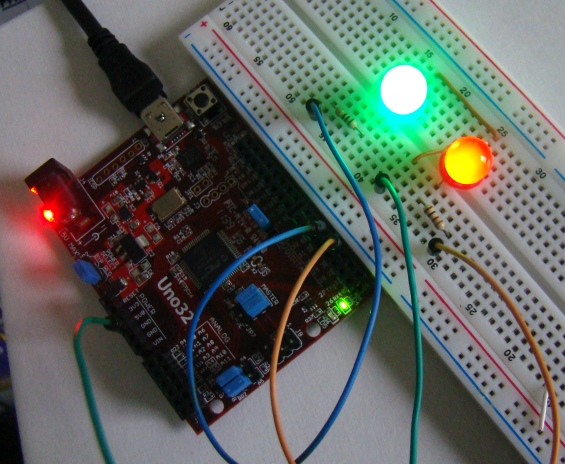
Output
In the program the duty cycle is varied from 1 to 255 in a step of 1. At the beginning, the red LED is driven with a PWM signal of duty cycle 255, which means it will be fully turned on. The PWM signal driving the green LED has the duty cycle of 1, which means it has minimum intensity. In every 10 ms, the duty cycle of the PWM signal driving the red LED is decreased by 1 and that of the green LED is increased by 1. After approximately 2550 ms, the brightness conditions are reversed, and the green LED is fully turned on. This repeats for ever creating fade in and out effects alternately.
LEDs operate at very low current and, therefore, it was feasible to drive them directly through the PWM outputs from the UNO32 board. For DC motor control, an external motor driver circuit, such as H-bridge, is required, which basically amplifies the low current PWM signals coming from the microcontroller pins into high current PWM signals capable of sourcing enough current to drive the motor.
|
|

Very good tutorial, with board pinout, great and detailed graphics… and firmware… thanks a lot.