Tinkering TI MSP430F5529

|
|
Alphanumerical LCD
Alphanumerical LCDs are probably the easiest devices to quickly project information visually. They are easy to use and cheap. To be able to use them, we do not need any additional hardware feature of a micro or any special communication hardware like I2C and SPI. Digital I/Os are what we need to use these displays. Just like my other tutorials, this tutorial includes three LCD examples – one with software SPI communication, one with software I2C communication and one with direct DIO-based 4-bit LCD interface.
Be sure to use 3.3V compatible LCD because most of them don’t operate at 3.3V power level. Most of the LCD are designed for 5V operation. It is okay to use 5V power supply for powering LCD if there is no other option. LCDs accept 0V – 3.3V logic level. However, there should be no way with which a 5V power supply/device can get connected with MSP430’s 3.3V power bus.
Code Example
lcd.h
#include "driverlib.h" #include "delay.h" #define LCD_RS_PORT GPIO_PORT_P8 #define LCD_RS_PIN GPIO_PIN1 #define LCD_EN_PORT GPIO_PORT_P8 #define LCD_EN_PIN GPIO_PIN2 #define LCD_D4_PORT GPIO_PORT_P2 #define LCD_D4_PIN GPIO_PIN3 #define LCD_D5_PORT GPIO_PORT_P3 #define LCD_D5_PIN GPIO_PIN7 #define LCD_D6_PORT GPIO_PORT_P2 #define LCD_D6_PIN GPIO_PIN6 #define LCD_D7_PORT GPIO_PORT_P4 #define LCD_D7_PIN GPIO_PIN0 #define LCD_RS_HIGH GPIO_setOutputHighOnPin(LCD_RS_PORT, LCD_RS_PIN) #define LCD_RS_LOW GPIO_setOutputLowOnPin(LCD_RS_PORT, LCD_RS_PIN) #define LCD_EN_HIGH GPIO_setOutputHighOnPin(LCD_EN_PORT, LCD_EN_PIN) #define LCD_EN_LOW GPIO_setOutputLowOnPin(LCD_EN_PORT, LCD_EN_PIN) #define LCD_DB4_HIGH GPIO_setOutputHighOnPin(LCD_D4_PORT, LCD_D4_PIN) #define LCD_DB4_LOW GPIO_setOutputLowOnPin(LCD_D4_PORT, LCD_D4_PIN) #define LCD_DB5_HIGH GPIO_setOutputHighOnPin(LCD_D5_PORT, LCD_D5_PIN) #define LCD_DB5_LOW GPIO_setOutputLowOnPin(LCD_D5_PORT, LCD_D5_PIN) #define LCD_DB6_HIGH GPIO_setOutputHighOnPin(LCD_D6_PORT, LCD_D6_PIN) #define LCD_DB6_LOW GPIO_setOutputLowOnPin(LCD_D6_PORT, LCD_D6_PIN) #define LCD_DB7_HIGH GPIO_setOutputHighOnPin(LCD_D7_PORT, LCD_D7_PIN) #define LCD_DB7_LOW GPIO_setOutputLowOnPin(LCD_D7_PORT, LCD_D7_PIN) #define clear_display 0x01 #define goto_home 0x02 #define cursor_direction_inc (0x04 | 0x02) #define cursor_direction_dec (0x04 | 0x00) #define display_shift (0x04 | 0x01) #define display_no_shift (0x04 | 0x00) #define display_on (0x08 | 0x04) #define display_off (0x08 | 0x02) #define cursor_on (0x08 | 0x02) #define cursor_off (0x08 | 0x00) #define blink_on (0x08 | 0x01) #define blink_off (0x08 | 0x00) #define _8_pin_interface (0x20 | 0x10) #define _4_pin_interface (0x20 | 0x00) #define _2_row_display (0x20 | 0x08) #define _1_row_display (0x20 | 0x00) #define _5x10_dots (0x20 | 0x40) #define _5x7_dots (0x20 | 0x00) #define DAT 1 #define CMD 0 #define dly 2 void LCD_DIO_init(void); void LCD_init(void); void LCD_send(unsigned char value, unsigned char mode); void LCD_4bit_send(unsigned char lcd_data); void LCD_putstr(char *lcd_string); void LCD_putchar(char char_data); void LCD_clear_home(void); void LCD_goto(unsigned char x_pos, unsigned char y_pos); void toggle_EN_pin(void); void toggle_io(unsigned char lcd_data, unsigned char bit_pos, unsigned int PORT, unsigned int PIN);
lcd.c
#include "lcd.h"
void LCD_DIO_init(void)
{
GPIO_setAsOutputPin(LCD_RS_PORT, LCD_RS_PIN);
GPIO_setAsOutputPin(LCD_EN_PORT, LCD_EN_PIN);
GPIO_setAsOutputPin(LCD_D4_PORT, LCD_D4_PIN);
GPIO_setAsOutputPin(LCD_D5_PORT, LCD_D5_PIN);
GPIO_setAsOutputPin(LCD_D6_PORT, LCD_D6_PIN);
GPIO_setAsOutputPin(LCD_D7_PORT, LCD_D7_PIN);
_delay_cycles(100);
}
void LCD_init(void)
{
LCD_DIO_init();
LCD_RS_LOW;
delay_ms(dly);
toggle_EN_pin();
LCD_send(0x33, CMD);
LCD_send(0x32, CMD);
LCD_send((_4_pin_interface | _2_row_display | _5x7_dots), CMD);
LCD_send((display_on | cursor_off | blink_off), CMD);
LCD_send((clear_display), CMD);
LCD_send((cursor_direction_inc | display_no_shift), CMD);
}
void LCD_send(unsigned char value, unsigned char type)
{
switch(type)
{
case DAT:
{
LCD_RS_HIGH;
break;
}
default:
{
LCD_RS_LOW;
break;
}
}
LCD_4bit_send(value);
}
void LCD_4bit_send(unsigned char lcd_data)
{
toggle_io(lcd_data, 7, LCD_D7_PORT, LCD_D7_PIN);
toggle_io(lcd_data, 6, LCD_D6_PORT, LCD_D6_PIN);
toggle_io(lcd_data, 5, LCD_D5_PORT, LCD_D5_PIN);
toggle_io(lcd_data, 4, LCD_D4_PORT, LCD_D4_PIN);
toggle_EN_pin();
toggle_io(lcd_data, 3, LCD_D7_PORT, LCD_D7_PIN);
toggle_io(lcd_data, 2, LCD_D6_PORT, LCD_D6_PIN);
toggle_io(lcd_data, 1, LCD_D5_PORT, LCD_D5_PIN);
toggle_io(lcd_data, 0, LCD_D4_PORT, LCD_D4_PIN);
toggle_EN_pin();
}
void LCD_putstr(char *lcd_string)
{
do
{
LCD_send(*lcd_string++, DAT);
}while(*lcd_string != '\0');
}
void LCD_putchar(char char_data)
{
LCD_send(char_data, DAT);
}
void LCD_clear_home(void)
{
LCD_send(clear_display, CMD);
LCD_send(goto_home, CMD);
}
void LCD_goto(unsigned char x_pos, unsigned char y_pos)
{
if(y_pos == 0)
{
LCD_send((0x80 | x_pos), CMD);
}
else
{
LCD_send((0x80 | 0x40 | x_pos), CMD);
}
}
void toggle_EN_pin(void)
{
LCD_EN_HIGH;
delay_ms(dly);
LCD_EN_LOW;
delay_ms(dly);
}
void toggle_io(unsigned char lcd_data, unsigned char bit_pos, unsigned int PORT, unsigned int PIN)
{
unsigned char temp = 0x00;
temp = (0x01 & (lcd_data >> bit_pos));
switch(temp)
{
case 0:
{
GPIO_setOutputLowOnPin(PORT, PIN);
break;
}
default:
{
GPIO_setOutputHighOnPin(PORT, PIN);
break;
}
}
}
main.c
#include "driverlib.h"
#include "delay.h"
#include "lcd.h"
void clock_init(void);
void show_value(unsigned char value);
void main(void)
{
unsigned char s = 0x00;
char txt1[] = {"MICROARENA"};
char txt2[] = {"SShahryiar"};
char txt3[] = {"MSP430F5529LP"};
char txt4[] = {"Launchpad!"};
WDT_A_hold(WDT_A_BASE);
clock_init();
LCD_init();
LCD_clear_home();
LCD_goto(3, 0);
LCD_putstr(txt1);
LCD_goto(3, 1);
LCD_putstr(txt2);
delay_ms(4000);
LCD_clear_home();
for(s = 0; s < 13; s++)
{
LCD_goto((1 + s), 0);
LCD_putchar(txt3[s]);
delay_ms(60);
}
for(s = 0; s < 10; s++)
{
LCD_goto((3 + s), 1);
LCD_putchar(txt4[s]);
delay_ms(60);
}
delay_ms(4000);
s = 0;
LCD_clear_home();
LCD_goto(3, 0);
LCD_putstr(txt1);
while(1)
{
show_value(s);
s++;
delay_ms(400);
};
}
void clock_init(void)
{
PMM_setVCore(PMM_CORE_LEVEL_3);
GPIO_setAsPeripheralModuleFunctionInputPin(GPIO_PORT_P5,
(GPIO_PIN4 | GPIO_PIN2));
GPIO_setAsPeripheralModuleFunctionOutputPin(GPIO_PORT_P5,
(GPIO_PIN5 | GPIO_PIN3));
UCS_setExternalClockSource(XT1_FREQ,
XT2_FREQ);
UCS_turnOnXT2(UCS_XT2_DRIVE_4MHZ_8MHZ);
UCS_turnOnLFXT1(UCS_XT1_DRIVE_0,
UCS_XCAP_3);
UCS_initClockSignal(UCS_FLLREF,
UCS_XT2CLK_SELECT,
UCS_CLOCK_DIVIDER_4);
UCS_initFLLSettle(MCLK_KHZ,
MCLK_FLLREF_RATIO);
UCS_initClockSignal(UCS_SMCLK,
UCS_REFOCLK_SELECT,
UCS_CLOCK_DIVIDER_1);
UCS_initClockSignal(UCS_ACLK,
UCS_XT1CLK_SELECT,
UCS_CLOCK_DIVIDER_1);
}
void show_value(unsigned char value)
{
unsigned char ch = 0x00;
ch = ((value / 100) + 0x30);
LCD_goto(6, 1);
LCD_putchar(ch);
ch = (((value / 10) % 10) + 0x30);
LCD_goto(7, 1);
LCD_putchar(ch);
ch = ((value % 10) + 0x30);
LCD_goto(8, 1);
LCD_putchar(ch);
}
Hardware Setup
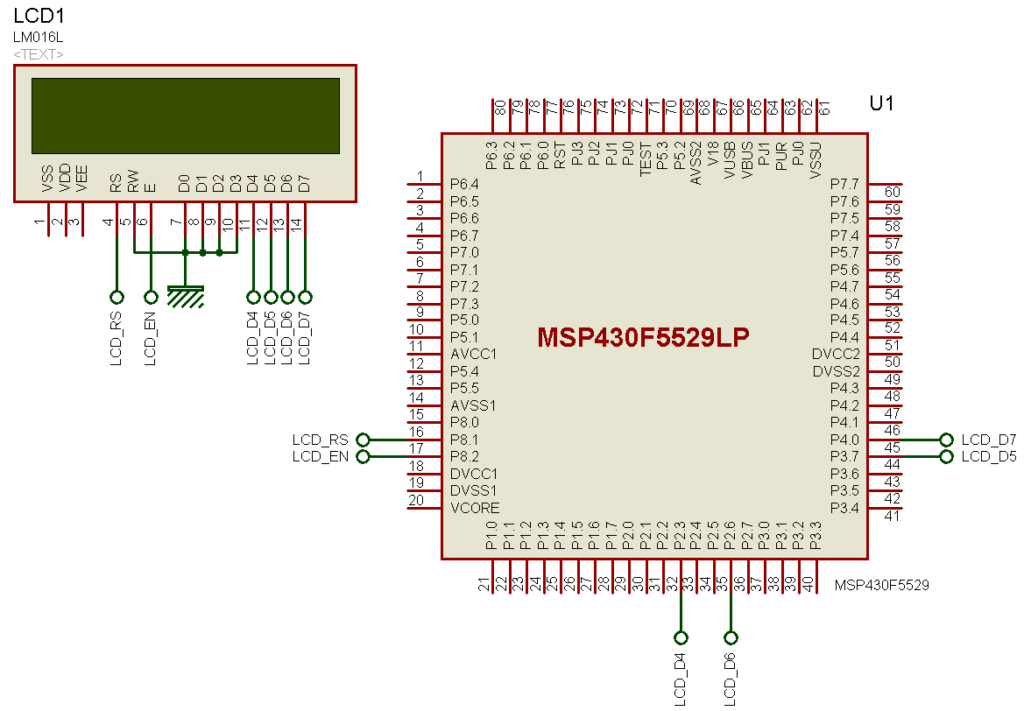
Explanation
Since alphanumerical displays utilize GPIOs, there’s hardly anything to explain here. Try not to use GPIOs that have alternate roles because you may never know when would you need their alternative functions.
Most popularly alphanumerical LCDs are driven in 4-bit data mode and this is what that has been done here. First let’s see some typical LCD instructions.
Since alphanumerical displays utilize GPIOs, there’s hardly anything to explain here. Try not to use GPIOs that have alternate roles because you may never know when would you need their alternative functions.
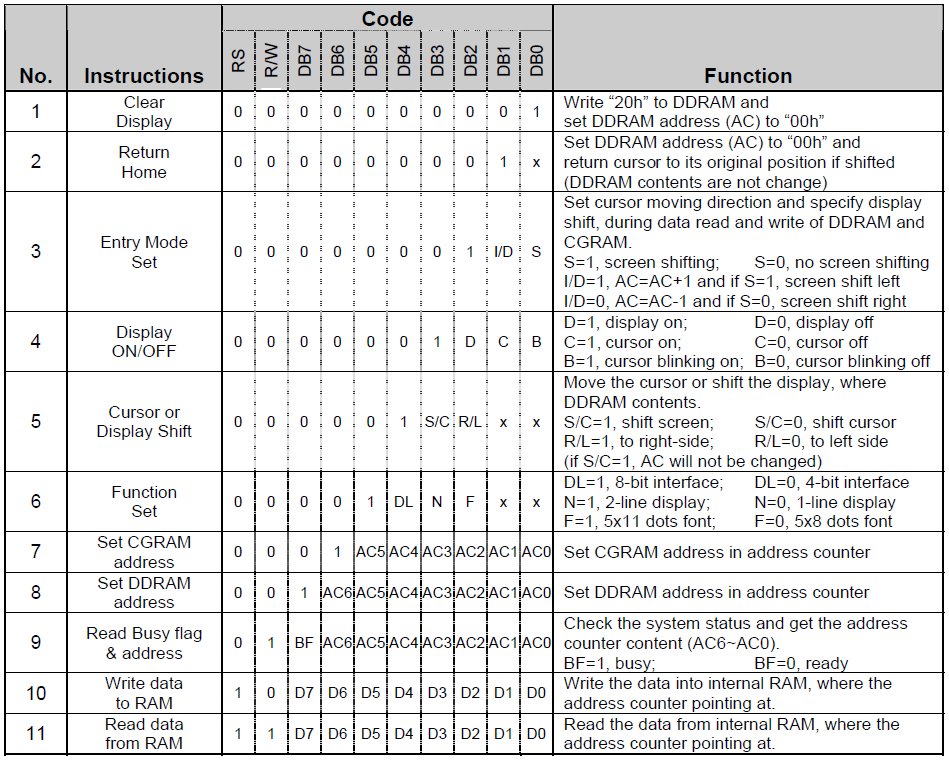
Most popularly alphanumerical LCDs are driven in 4-bit data mode and this is what that has been done here. First let’s see some typical LCD instructions.
#define LCD_RS_PORT GPIO_PORT_P8 #define LCD_RS_PIN GPIO_PIN1 #define LCD_EN_PORT GPIO_PORT_P8 #define LCD_EN_PIN GPIO_PIN2 #define LCD_D4_PORT GPIO_PORT_P2 #define LCD_D4_PIN GPIO_PIN3 #define LCD_D5_PORT GPIO_PORT_P3 #define LCD_D5_PIN GPIO_PIN7 #define LCD_D6_PORT GPIO_PORT_P2 #define LCD_D6_PIN GPIO_PIN6 #define LCD_D7_PORT GPIO_PORT_P4 #define LCD_D7_PIN GPIO_PIN0
This declaration in the LCD header file is very important as it states GPIO pin purposes.
Initialization of the LCD is done by going through the steps in the following program flow graph and manipulating the LCD pins accordingly.

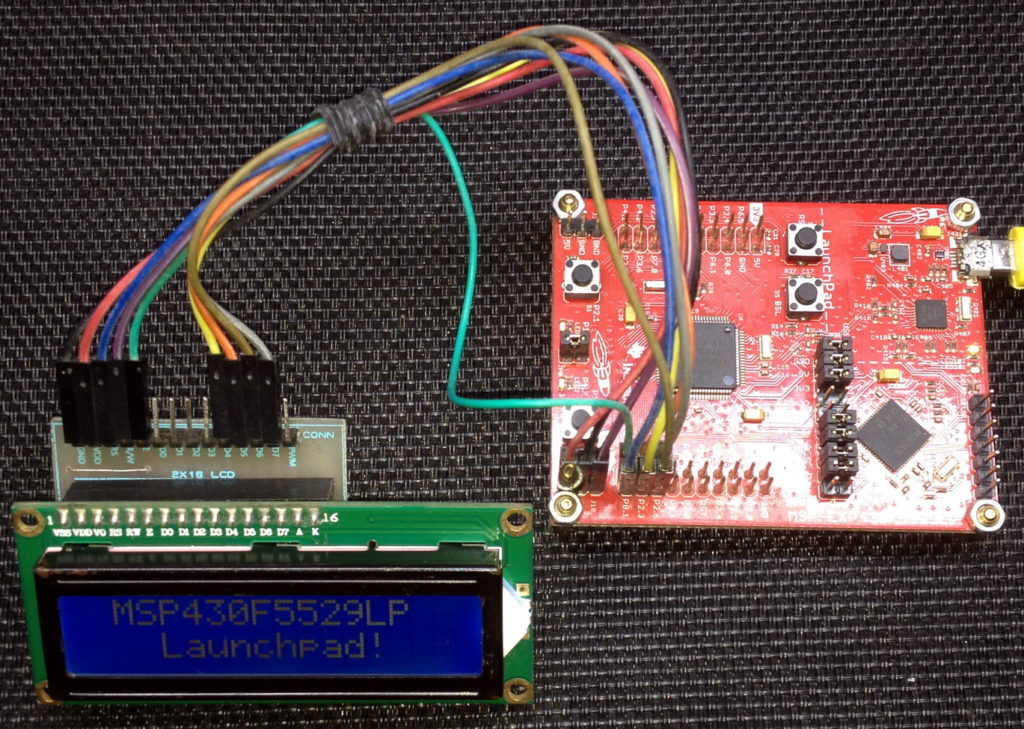
Demo
|
|
Hello, what software are you using for the Hardware setup images and does it support simulation for the MSP430F5529
I used Proteus VSM for drawing schematics but it doesn’t support simulation.
Hi,
Im interfacing MSP430F5529 with MAX17055 fuel guage. while reading 16 bit value, the first byte im receiving is 0. so while reading multiple registers continuously the data exchange is happening, but im getting the correct data. Can anyone suggest me what will be the issue? why im getting 0 in first byte?
read16_bit data code:
uint16_t value = 0;
USCI_B_I2C_setslaveaddress(USCI_B1_BASE, slave_address);
USCI_B_I2C_setmode(USCI_B1_BASE, USCI_B_I2C_TRANSMIT_MODE);
USCI_B_I2C_masterSendStart(USCI_B1_BASE);
while (!USCI_B_I2C_masterSendStart(USCI_B1_BASE));
USCI_B_I2C_mastterSendSingleByte(USCI_B1_BASE, reg_address);
USCI_B_I2C_setslaveaddress(USCI_B1_BASE, slave_address);
USCI_B_I2C_setmode(USCI_B1_BASE, USCI_B_I2C_TRANSMIT_MODE);
USCI_B_I2C_masterReceiveMultiByteStart(USCI_B1_BASE);
uint8_t lb = USCI_B_I2C_masterReceiveMultiByteNext(USCI_B1_BASE);
uint8_t hb = USCI_B_I2C_masterReceiveMultiByteFinish(USCI_B1_BASE);
while (USCI_B_I2C_isBusBusy(USCI_B_BASE));
value = lb << 8;
value |= hb;
return value;
In code, after sending reg address, it will be recieve mode. its a type mistake
Hi, im trying to send the command from the terminal view. i can able to send the command and tried to blink p1.0 led in msp430f5529 controller, its working fine. And im using led driver IS31FL3236A interfaced with msp430f5529 controller, i can able to interface im getting the expected output.
now i need to send the command from seriak monitor based on that command i2c communication need to start. both communication are working fine, when it runs separately. its not working when i tried to combine.
any one had any idea, why it is happening or what will be the issue?
It could be due to:
1. conflicts in clock settings
2. hardware conflict like pin mapping
3. code is getting stuck or waiting for one communication line to finish
4. use of polling method instead of interrupt-driven coding
Hi, thank you for the respose.
Do I need to use different clock initialization for I2C and UART communication? if YES, can you explain how to do that?
I mean check which clock has been set for UART and I2C…. Is it SMCLK, MCLK, etc and is it tuned to right frequency required by the respective hardware?
Is there any example on how to implement polling method in uart?
Why go for polling method when it is a blocking method of coding? It is better to use interrupts instead at least for UART receive.
yes!! currently in my code, only for uart im using interrupts to recieve command from serial monitor. Im not using interrupt for I2C communication.
so the issue is must be in clock initialization. right?
For UART, im using USCI_A1_BASE. and for I2C, im using USCI_B1_BASE.
And another thing i need to ask is, in uart when i tried blink led(p1.0) in msp430f5529 by passing command. here, without clock I’m getting output. how it is possible?
And for both i2c and uart i gave SMCLK with 1Mhz
I am surprised and happy to find this tutorial on the F5529 as TI makes a lot of different devices.
Thank you very much for putting in the extra knowledge in each segment, made reading worthwhile.
Good Work!
lovely tutorial but to be honest I don’t think I’d be investing my time on this board to start with it’s not cheap and readily available as the stm32 boards can you please do more tutorials on stm32 board’s and the stc micros thanks
Hello, I try to program MSP430FR6047 but i get error “the debug interface to the device has been secured”. when flashing using uniflash and when program using CCS this happen. can you help me to solve this problem
You can try “On connect, erase user code and unlock the device” option.
Pingback: Tinkering TI MSP430F5529 – gStore
Hello
I am doing project of msp430g2553 interface(using i2c communication) with temp 100(temperature sensor) and try to read the temperature in dispaly(16*2) but didn’t get the out put (using code composer studio) can u share me any example code for this project
Thank you sir,
Which sensor? Did you use pullup resistors for SDA-SCL pins?
Where is lcd_print.h?
All files and docs are here:
https://libstock.mikroe.com/projects/view/3233/tinkering-ti-msp430f5529
You want the truth? TI makes and sell “underpowered micros”, you know? Low everything, not only the power but also peripherals. So the price is not justified.
Otherwise, if I’ll move there, I’ll introduce them to my small hobby projects – there are still some advantages.
I may even make a visual configuration tool of my own for them…
Yeah the prices of TI products are higher than other manufacturers but I don’t think the hardware peripherals are inferior.
Not inferior but in not enough numbers compared to STM32.
True